Current Status of Carbon Emissions
The current state of carbon emissions is one of the major environmental challenges facing the world today. Despite some progress in emission reduction, global carbon emissions remain at high levels, and their impact on climate change continues to intensify.
- Total Carbon Emissions Are Still Rising:
According to the latest data, global carbon emissions reached a historic high in 2023. Although there are trends of reduction in some regions, such as Europe, the increase in carbon emissions driven by emerging economies like China and India has outweighed these reduction efforts. - Major Carbon Emitting Countries:
- China: China is the largest carbon emitter in the world, accounting for about 30% of global carbon emissions. This is primarily due to its enormous energy demand and continued reliance on coal.
- United States: The U.S. is the second-largest carbon emitter, responsible for approximately 15% of global carbon emissions. Although the U.S. has made progress in renewable energy, its high consumption patterns continue to drive carbon emissions.
- India: India’s rapid industrialization has led to a significant increase in its carbon emissions, making it the third-largest carbon emitter globally.
- China: China is the largest carbon emitter in the world, accounting for about 30% of global carbon emissions. This is primarily due to its enormous energy demand and continued reliance on coal.
- Sector Distribution:
- Energy Sector: The burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) remains the primary source of carbon emissions, accounting for about 75% of global emissions.
- Transportation: Emissions from vehicles, airplanes, ships, and other modes of transport account for about 20% of total carbon emissions, with an upward trend.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Industries such as steel, cement, and chemicals also contribute significantly to emissions, especially in emerging economies.
- Energy Sector: The burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) remains the primary source of carbon emissions, accounting for about 75% of global emissions.
- Link Between Carbon Emissions and Economic Development:
Carbon emissions are closely related to economic activity. As the global economy recovers and grows, particularly with the economic development of emerging markets, carbon emissions tend to increase accordingly.
Impact of Carbon Emissions
Since the Industrial Revolution, carbon emissions have led to a significant increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations, rising from approximately 280 ppm before the Industrial Revolution to over 400 ppm today. These emissions have intensified global warming, resulting in more frequent extreme weather events, rising sea levels, changes in ecosystems, and an increased risk of species extinction.
Mitigation Measures
As the impact of carbon emissions on the climate becomes increasingly evident, global efforts to reduce emissions have been initiated. These include the signing of the Paris Agreement, the development of renewable energy, advancements in energy efficiency technologies, and the establishment of carbon trading markets. However, to achieve the goal of limiting global temperature rise to within 1.5°C, much larger-scale global cooperation and transformative actions are required.
Challenges in Emission Reduction
- Policy and Technological Barriers:
- Although the Paris Agreement aims to limit global temperature rise to within 1.5°C, many countries have yet to develop or implement sufficiently robust emission reduction policies.
- While the adoption of clean energy technologies is progressing rapidly, it still faces challenges such as high costs, technological bottlenecks, and infrastructure limitations.
- Unequal Resource Distribution:
Developing countries often face greater economic pressures and lack the necessary funding and technology to implement effective emission reduction measures. - Energy Transition:
The global energy structure is still heavily reliant on fossil fuels. Transitioning to renewable energy requires significant investment and time and faces political, economic, and social resistance.
Future Trends
- Accelerated Energy Transition:
With advancements in renewable energy technologies and decreasing costs, the global energy structure is expected to gradually shift toward a low-carbon economy dominated by renewable energy. - Carbon Capture and Storage Technology:
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) technology is expected to play a more significant role in the future, helping to reduce industrial carbon emissions that are difficult to avoid. - Strengthened Global Cooperation:
International cooperation will be key to addressing carbon emissions, particularly in climate financing, technology transfer, and policy coordination.
Overall, the current state of carbon emissions reveals that the world still faces significant challenges in addressing climate change, and urgent action is needed to prevent the worst climate outcomes.
Carbon Credits and Carbon Markets
Carbon credits and carbon markets are crucial tools in the global effort to combat climate change and promote the reduction of carbon emissions. They provide economic incentives for businesses and governments to meet their emission reduction targets through market mechanisms.
What Are Carbon Credits/Offsets?
A carbon credit is a tradable certificate or permit representing the reduction of one ton of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases (GHGs). These credits are typically awarded by governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), or private entities based on specific emission reduction projects, such as reforestation, renewable energy initiatives, or energy efficiency improvements. When an entity invests in a carbon offset program, it receives carbon credits or offset credits, which represent the net climate benefits generated for another entity.
- One unit of carbon credit typically corresponds to the reduction or avoidance of one ton of CO2 equivalent (CO2e).
- Carbon credits, once certified by government or independent verification bodies, can be traded on international carbon markets to offset a company’s carbon emissions and achieve carbon neutrality.
Who Can Sell Carbon Credits?
Carbon credits can only be sold or purchased by companies and governments. However, carbon offsets are carbon credits that can be sold on the voluntary carbon market. The voluntary carbon market allows entities participating in emission reduction projects to sell non-regulated credits. Anyone can purchase these credits.
- Carbon credits are sold by governments to companies and can be resold on regulated carbon credit markets.
- Carbon offsets are sold by organizations, projects, or individuals in the voluntary carbon credit market to fund their green projects.
Various businesses and individuals can sell these carbon offsets based on their participation in carbon sequestration or carbon storage programs. For example, landowners can sell carbon credits by registering their land in projects such as reforestation, afforestation, or other carbon removal initiatives, using the proceeds to cover their operational costs.
Why Do Companies Purchase Carbon Credits?
Companies purchase carbon credits to legally emit more greenhouse gases (GHGs). They also buy carbon offsets, which allow them to achieve a “net-zero carbon emission” rate.
As the climate crisis intensifies, there is growing pressure from the public and institutions for companies to make these net-zero commitments. These commitments involve companies pledging to reduce or offset the carbon emissions generated by their operations.
For some companies, it is feasible to reduce emissions by changing business practices, but for many, completely eliminating emissions is impractical. Carbon offsets fund emission reduction activities such as reforestation or nature conservation, providing an alternative to entirely eliminating their own emissions.
Global Carbon Credit Initiatives
The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) introduced a carbon credit proposal in 1997 to reduce global carbon emissions, known as the Kyoto Protocol. This agreement set binding emission reduction targets for its signatory countries. The Marrakech Accords further detailed the operational mechanisms of this system.
The Kyoto Protocol divided countries into industrialized and developing nations. Industrialized nations, known as “Annex I” countries, operated within their own emissions trading markets. If a country’s emissions fell below its target level, it could sell the remaining credits to other countries that failed to meet their Kyoto targets through an Emission Reduction Purchase Agreement (ERPA).
For developing nations, the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) issued Certified Emission Reductions (CERs) as carbon credits. Developing countries could earn these credits by supporting sustainable development projects, and CERs could be traded in a separate market.
What is the Carbon Credit Market?
A carbon credit market is a marketplace that allows the trading of carbon credits. These markets regulate carbon emissions between companies or countries by buying and selling carbon credits, facilitating the achievement of global emission reduction goals. There are two types of carbon credit markets:
- Compliance Markets:
- These markets are established based on international or national laws and regulations, primarily serving regulated companies and countries. Examples include the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) under the Kyoto Protocol and the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS).
- In compliance markets, companies and countries must purchase sufficient carbon credits to meet regulatory requirements. If their emissions exceed the allocated limits, they can buy additional carbon credits from the market to compensate.
- These markets are established based on international or national laws and regulations, primarily serving regulated companies and countries. Examples include the Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) under the Kyoto Protocol and the European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS).
- Voluntary Markets:
- Voluntary markets are not governed by government regulations, allowing companies and individuals to voluntarily purchase carbon credits to offset their carbon emissions and achieve carbon neutrality.
- Voluntary markets are often driven by companies wishing to demonstrate environmental commitment, and some individuals or organizations buy carbon credits to fulfill social responsibility or meet Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) standards.
- Voluntary markets are not governed by government regulations, allowing companies and individuals to voluntarily purchase carbon credits to offset their carbon emissions and achieve carbon neutrality.
The Role of Carbon Credits and Carbon Credit Markets in Carbon Emissions
- Incentivizing Emission Reductions:
Carbon credits provide economic incentives for companies to invest in emission reduction technologies and projects. By selling carbon credits, companies can generate additional revenue, which can be reinvested into environmental projects. - Resource Allocation and Efficiency:
Carbon credit markets allocate resources through market mechanisms to companies and countries that can reduce carbon emissions at the lowest cost, thereby enhancing global emission reduction efficiency. - Driving Global Carbon Neutrality:
Carbon credits and carbon credit markets are essential tools for achieving carbon neutrality. By purchasing carbon credits, companies can offset their unavoidable emissions and reach carbon-neutral goals. - International Cooperation:
Carbon credit markets foster international cooperation. Developing countries can gain financial support for low-carbon economic development by exporting carbon credits. - Regulation and Compliance:
In compliance markets, carbon credits help ensure that companies adhere to emission regulations and assist governments in meeting their emission reduction targets.
Overall, carbon credits and carbon credit markets integrate environmental responsibility with market behavior through economic means, providing a flexible and effective mechanism for global emission reduction and climate change mitigation.
Opportunities and Challenges
Carbon credits and carbon credit markets, as market mechanisms to combat climate change, present a range of opportunities and challenges. These opportunities and challenges reflect their potential in global emission reduction efforts while also highlighting key issues that need to be addressed.
Opportunities
- Growing Global Demand for Emission Reductions:
With the advancement of the Paris Agreement and various national carbon neutrality goals, the demand for carbon credits has significantly increased. This creates substantial opportunities for the expansion and maturation of carbon credit markets. - Technological Innovation Driving Carbon Credit Development:
Innovations in technology, such as blockchain, AI, and big data, can enhance the transparency, traceability, and efficiency of carbon credits, reducing transaction costs and increasing market trust. - Key Role in Corporate ESG Strategies:
More and more companies are incorporating carbon credits into their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) strategies to achieve carbon neutrality. This promotes corporate participation in voluntary carbon markets, bringing more liquidity and dynamism to the market. - Promotion of Renewable Energy and Natural Resource Conservation:
Carbon credits can incentivize investments in renewable energy projects and natural resource conservation projects, such as forest carbon sinks, which not only help reduce emissions but also promote the protection and restoration of ecosystems. - International Cooperation and Capital Flow:
Carbon credit markets facilitate cooperation between developed and developing countries. Through carbon credit trading, developing countries can obtain financial support to drive low-carbon technology and sustainable development.
Challenges
- Lack of Market Standardization and Regulation:
The standards and regulations of carbon credit markets are still inconsistent globally, making it difficult for markets in different regions and countries to interact, which weakens market liquidity and efficiency. - Certification and Trust Issues Regarding Carbon Credit Quality:
The quality of different carbon credits may vary, especially in voluntary markets. Some carbon credits may fail to achieve genuine emission reductions, damaging the market’s credibility and trust. - Risk of Double Counting:
Double counting occurs when the same carbon reduction project is credited to the emission reductions of multiple parties, potentially leading to an overestimation of overall reduction effects. Addressing this issue requires stronger regulation and transparency. - Volatility in Carbon Credit Prices:
The carbon credit market is subject to significant price volatility, which may affect companies’ confidence in long-term emission reduction plans. Price instability can also lead to hesitation among market participants, hindering market development. - Political and Legal Risks:
The development of carbon credit markets heavily relies on policy support and international agreements. Changes in domestic or international policies could impact the market’s stability and predictability. - Limited Participation from Developing Countries:
Many developing countries lack the technology, funding, and capacity building needed to participate in carbon credit markets, limiting the global scale and impact of the market. - Risk of Greenwashing:
Some companies may purchase carbon credits to superficially achieve carbon neutrality without actually reducing their emissions. This “greenwashing” behavior could undermine the market’s credibility.
Carbon credits and carbon credit markets have tremendous potential to become key tools in global emission reduction. However, to fully realize their potential, it is essential to overcome current challenges, particularly in standardization, transparency, trust, and global cooperation. As the market matures and technology advances, these opportunities and challenges will collectively shape the future of carbon credit markets.
Introduction to ccarbon
Founded in 2019, the ccarbon team has been dedicated to research in the carbon reduction industry and related vocational education. Their carbon reduction and emission mitigation vocational education programs cover multiple industries, including electricity, cement, steel, paper, aviation, non-ferrous metals, and petrochemicals. The educational content spans various dimensions, such as carbon emission management, consulting, trading, verification, accounting, and detection. ccarbon‘s vocational education business has achieved stable profitability, annually supplying a large number of professionals to the industry. Additionally, to explore more possibilities in carbon asset management, the ccarbon team established the ccarbon Climate Fintech Labs.
ccarbon Climate Fintech Labs
Located in London, UK, the ccarbon Climate Fintech Labs (hereafter referred to as ccarbon or ccarbon Labs) also serves as ccarbon‘s operational headquarters. Leveraging the professional knowledge and industry experience of the ccarbon team, the laboratory continuously explores global carbon reduction solutions to ensure the feasibility, compliance, and scalability of ccarbon’s carbon inclusivity management solutions.
ccarbon Labs are also the issuer of the global carbon asset digital token CCT and its financial derivatives. By utilizing London’s open and inclusive financial policies and its rich pool of fintech talent, ccarbon empowers CCT to serve as a universally applicable, compliant, and scalable financial instrument.
Role of ccarbon Labs
ccarbon plays multiple roles in different stages of carbon emissions to address the complexities of achieving carbon reduction and environmental protection. Primarily, ccarbon operates in three key areas:
- Carbon Vocational Education
- Carbon Inclusivity Management Solutions Provider
- Global Carbon Asset Climate Finance Management Foundation
1. Carbon Vocational Education:
ccarbon’s carbon asset vocational education aims to provide individuals, businesses, and professionals with the knowledge, skills, and expertise needed to understand and address carbon emissions. This includes training talent to work in fields related to climate change mitigation, such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, carbon accounting, and sustainable management. Their vision is to empower individuals to actively contribute to reducing carbon emissions through their careers.
2. Carbon Inclusivity Management Solutions Provider:
As a carbon inclusivity management solutions provider, ccarbon focuses on developing and implementing solutions to reduce and mitigate carbon emissions across various industries. This includes deploying innovative technologies, providing tailored integrated strategies, promoting sustainable practices, and collaborating with stakeholders to achieve emission reduction goals. Industries covered include 3D printing, artificial intelligence, smart production, intelligent manufacturing, new material development, and fintech.
3. Global Carbon Asset Climate Finance Management Foundation:
ccarbon is dedicated to managing carbon assets, facilitating carbon credit trading, driving sustainable development through emission reduction projects, advocating for policies that incentivize carbon reduction, and ensuring the integrity and transparency of carbon credits. Their vision includes promoting sustainable development goals through strategic management of carbon assets within a legitimate financial system, addressing climate change challenges.
Additionally, the ccarbon Global Carbon Inclusivity Management Foundation is committed to spreading knowledge and building consensus on environmental protection, carbon assets, and climate fintech:
- Hosting scientific summits in developed economies to research and practice carbon inclusivity finance, empowering every participant in society.
- Establishing volunteer communities in developing economies to truly implement low-carbon industries, low-carbon economies, and low-carbon lifestyles at the early stages of local industrial economic development.
These three areas encompass vocational education, research and development, and management in the carbon asset field. The goal is to take a comprehensive approach to addressing climate change and achieving a low-carbon and sustainable future, from educating future leaders and professionals to providing practical emission reduction solutions and responsibly managing carbon assets.
Join us in safeguarding the future of our green planet:
ccarbon: Global Carbon Inclusivity Management Official Website: https://ccarbon.world
ccarbon X (Twitter): https://x.com/ccarbonWorld
ccarbon Telegram Channel: https://t.me/ccarbonWorld
ccarbon Solutions
In the “Opportunities and Challenges” section of this document, it is noted that while carbon credits (carbon emission rights) possess certain commodity characteristics, their nature as a form of rights differentiates their trading significantly from common commodities like gold, soybeans, and crude oil. ccarbon aims to leverage the financial attributes of global carbon credit commodity trading to mitigate risks in carbon asset transactions, allowing every individual, whether a small business or an individual, to participate in the carbon asset market. Simultaneously, ccarbon sets economic incentives for every step of carbon reduction actions, with the belief that “a good environmental solution must be people-centric.” This approach benefits society, enterprises, and individuals:
- For society: It promotes the effective dissemination and execution of carbon reduction behaviors, effectively curbing the spread of the greenhouse effect.
- For enterprises: It provides the opportunity to hedge potential climate risks effectively through CCT financial derivatives.
- For individuals: It enables convenient certification, trading, and management of personal carbon assets through the ccarbon Global Carbon Inclusivity Management Platform.
For small business owners and individuals, the most challenging aspect of carbon inclusivity management is that the earnings from carbon assets barely cover the cost of carbon asset certification. For example, one hectare of forest land in Europe (1,200 – 1,500 trees) can only sequester 10 tons of CO2 per year, and the resulting revenue cannot cover the cost of professionally verifying the carbon sequestration capacity of the forest land (under the premise of not harming the local natural ecology, using local natural methods, employing local conservation talent, etc.), let alone the costs involved in consulting, verification, testing, and trading during the process of carbon inclusivity management.
However, ccarbon, through the universality, compliance, and scalability of CCT and its derivative financial products, provides a systematic and complete solution for every participant in low-carbon actions, lowering the threshold for participation in low-carbon activities, and significantly reducing the hidden costs for each participant through the economic scale effects generated by the number of people involved.

Carbon Credit Token (CCT)
As a financial instrument, the Carbon Credit Token (CCT) uses ccarbon laboratory’s global carbon credits (acquired through collection, trading, etc.) as underlying assets to provide a complete standard for the carbon asset market within the fair value range of its underlying assets. This unified standard also allows the ccarbon laboratory to reduce the substantial costs required for carbon asset certification for individuals or small business owners through economic scale. Additionally, due to the diversity of CCT’s underlying assets (various carbon assets and derivatives from exchanges worldwide), CCT can also facilitate exchange transactions between carbon assets from specific countries or regions, ensuring the universal applicability and compliance of the CCT token’s economy. From a financial perspective, CCT does not necessarily have to be a cryptocurrency; it can be understood as a financial instrument based on global carbon assets. Due to the transparency, immutability, and ease of participation provided by blockchain technology, ccarbon laboratory favors the use of cryptocurrency technology to realize the function of this financial instrument.
CCT Tokenomics

Total Supply of CCT: 580 million CCT
- Carbon Credit Conversion (40%: 232 million CCT):
This allocation is distributed to individuals through the ccarbon App. Users can convert carbon credits generated by sustainable actions into CCT tokens. The conversion rate between carbon credits and CCT will vary depending on the price at the time and local compliance requirements.
In the first phase of the CCT Carbon Credit Conversion Pool, 87 million CCT will be released (483,333 per day). If the daily carbon mining volume does not reach the total release amount of 483,333 CCT, 30% of the remaining release amount will be destroyed, and 70% will be returned to the pool.
Carbon reduction participants will primarily engage in carbon reduction through smart low-carbon devices(ccarbon Sneakers and ccarbon Smart Ring etc..), collecting carbon credits with a daily maximum of 34 units (equivalent to 10,200 steps). Even without step tracking, users will receive 10 carbon points per day as an environmental incentive. When each pair of shoes produces the 1,020th CCT, the mining efficiency of the product is halved.
Additionally, as part of the ccarbon laboratory’s solutions, the laboratory will collect 40% of the sales revenue of each pair of shoes as a licensing fee to support CCT’s market value and liquidity management. - Staking Pool (30%: 174 million CCT):
- Reserved for long-term maintenance of CCT’s fundamental value and volatility management. For example, during the pre-sale (IDO), 5% of the total CCT supply will be newly issued to the public market, and the ccarbon Foundation will be responsible for continuously purchasing or collecting corresponding underlying carbon assets within six months from the issuance date to support the CCT issuance.
- The pool includes staking (15-20 years), token listing fees, and the implementation of financial technology applications that comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CFT) regulations.
- In the future, part of the ccarbon laboratory’s profits will also be reinvested in environmental startups and distributed as rewards within the community to support sustainable development and reward staking participants.
- Reserved for long-term maintenance of CCT’s fundamental value and volatility management. For example, during the pre-sale (IDO), 5% of the total CCT supply will be newly issued to the public market, and the ccarbon Foundation will be responsible for continuously purchasing or collecting corresponding underlying carbon assets within six months from the issuance date to support the CCT issuance.
- Liquidity Pool (10%: 58 million CCT):
Used to provide liquidity for CCT trading on various platforms, ensuring market stability and accessibility. - Public Presale (IDO) (5%: 29 million CCT):
Reserved for the Initial Decentralized Offering (IDO) to promote broader community participation and early adoption. - Airdrops and Interaction (Beta) (4%: 23 million CCT):
Used for promotional activities, community engagement, and testing purposes during the beta phase of the ccarbon project. - Contributor Community and Development Team (6%: 35 million CCT):
- Reserved as incentives for teams and contributors who contribute to the development and growth of the ccarbon ecosystem over ten years.
- Additionally, this portion will be used as governance tokens within the ccarbon community, rewarding active community members.
- Reserved as incentives for teams and contributors who contribute to the development and growth of the ccarbon ecosystem over ten years.
- Institutional Investment Pool (5%: 29 million CCT):
Specifically designated for strategic partners involved in the ccarbon program and institutional investors seeking to support the ccarbon program for the long term (five years or more).
CCT and Its Underlying Assets
ccarbon plays a crucial role in ensuring the stability and integrity of the crypto carbon token (CCT) by managing its correlation with the underlying global carbon credit assets traded. The following details the key responsibilities and mechanisms involved:
- Maintaining Underlying Asset Correlation:
- Objective: Ensure that each CCT token is backed by actual carbon credit assets.
- Implementation: Regular audits and oversight to verify that actual carbon credits support CCT.
- Asset Management: The foundation manages the leverage and ratio of the underlying carbon assets, which is crucial for:
- Supporting CCT Value: Adjusting asset holdings to maintain a stable and reliable value for each CCT token, reflecting its actual carbon credit backing.
- Ensuring Price Stability: Preventing significant fluctuations in CCT prices by managing asset allocation.
- Enhancing Liquidity: Adjusting asset positions to ensure sufficient reserves to facilitate trading and maintain CCT’s market liquidity.
- Objective: Ensure that each CCT token is backed by actual carbon credit assets.
- Leverage and Ratio Management:
- Strategic Management: Determining the optimal leverage ratio of carbon credits (asset allocation of total holdings).
- Risk Management: Mitigating asset volatility risks by adjusting leverage and asset allocation accordingly.
- Liquidity Support: Providing liquidity and stability to CCT trading platforms by managing the availability and distribution of carbon assets.
- Strategic Management: Determining the optimal leverage ratio of carbon credits (asset allocation of total holdings).
- Ensuring Value and Transparency:
- Auditing and Oversight: Regular audits to ensure the transparency and compliance of CCT’s carbon credit backing.
- Reporting: Providing stakeholders with transparent reports on asset management and CCT valuation.
- Future Profits: Profits obtained through the market value management process will be distributed as economic incentives to the community and reinvested in environmental startup projects across various industries.
- Auditing and Oversight: Regular audits to ensure the transparency and compliance of CCT’s carbon credit backing.
Impact on CCT Value and Liquidity
- Value Stability: By managing the correlation with carbon assets and adjusting leverage and ratios, ccarbon aims to stabilize the value of CCT, ensuring it accurately reflects the underlying carbon credit assets.
- Market Liquidity: Proper asset reserve management and strategic asset allocation support CCT trading liquidity, making it easier for users to buy and sell tokens across various platforms.
ccarbon’s role in controlling the leverage and ratio of underlying carbon credit assets is crucial for maintaining the value, price stability, and liquidity of the crypto carbon token (CCT). This governance ensures that CCT remains a reliable and effective tool for participating in the global carbon credit market, aligning with ccarbon‘s mission to combine finance with environmental impact to achieve a sustainable future.
CCT Climate Finance Derivatives:
CCT Climate Finance Derivatives are specialized financial instruments designed to manage and hedge financial risks associated with climate change. These derivatives help businesses, investors, and government institutions manage risks and protect assets in the face of economic challenges posed by climate change. The ccarbon Global Climate Finance Laboratory may allow individuals, within a controlled risk environment, to hedge climate and environmental risks or profit through participation in CCT climate finance derivatives in the form of NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks), RWAs (Real World Assets), and more:
- CCT Carbon Credit Derivatives
- Carbon Credit Trading: Carbon credits are one of the most common climate finance derivatives. Companies can purchase carbon credits to offset their carbon emissions. These credits are typically traded in regulated or voluntary carbon markets.
- Carbon Futures and Options: These contracts allow companies or investors to buy or sell carbon credits at a fixed price in the future, thereby hedging against the risk of carbon credit price fluctuations.
- Carbon Credit Trading: Carbon credits are one of the most common climate finance derivatives. Companies can purchase carbon credits to offset their carbon emissions. These credits are typically traded in regulated or voluntary carbon markets.
- CCT Climate Risk Insurance
- Weather Derivatives: These derivatives are based on weather data (such as temperature, precipitation, etc.) and can help industries like agriculture and energy hedge against economic risks brought on by extreme weather events. For example, temperature futures can hedge against the impact of unusually high or low temperatures on crop yields.
- Weather Derivatives: These derivatives are based on weather data (such as temperature, precipitation, etc.) and can help industries like agriculture and energy hedge against economic risks brought on by extreme weather events. For example, temperature futures can hedge against the impact of unusually high or low temperatures on crop yields.
- CCT Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs)
- Green Certificate Trading: Companies can purchase renewable energy certificates to offset their energy consumption. These certificates represent electricity produced from renewable sources such as wind or solar energy. Such derivatives help promote the development of renewable energy.
- Green Certificate Trading: Companies can purchase renewable energy certificates to offset their energy consumption. These certificates represent electricity produced from renewable sources such as wind or solar energy. Such derivatives help promote the development of renewable energy.
- CCT Green Bonds
- Green Bonds: These bonds are specifically issued to raise funds for environmental projects, such as renewable energy facilities, clean technologies, and sustainable development projects. The proceeds from green bonds are typically used for climate change mitigation projects.
- Green Bonds: These bonds are specifically issued to raise funds for environmental projects, such as renewable energy facilities, clean technologies, and sustainable development projects. The proceeds from green bonds are typically used for climate change mitigation projects.
- CCT Catastrophe Bonds (Cat Bonds)
- Catastrophe Bonds: These bonds provide insurance companies and reinsurance companies with a way to transfer catastrophic risk. If a specific natural disaster (such as a hurricane or earthquake) occurs, the bond’s principal is used to cover related losses.
- Catastrophe Bonds: These bonds provide insurance companies and reinsurance companies with a way to transfer catastrophic risk. If a specific natural disaster (such as a hurricane or earthquake) occurs, the bond’s principal is used to cover related losses.
- CCT Natural Capital Derivatives
- Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES): These derivatives involve payments to maintain or enhance the ecosystem services provided by natural capital (such as forests, water resources, and soil fertility). For example, a company might pay farmers to protect forests to offset its carbon emissions.
- Payments for Ecosystem Services (PES): These derivatives involve payments to maintain or enhance the ecosystem services provided by natural capital (such as forests, water resources, and soil fertility). For example, a company might pay farmers to protect forests to offset its carbon emissions.
- CCT Forest and Land Use Derivatives
- REDD+ Derivatives: REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) project derivatives allow companies and countries to trade forest carbon credits in global markets, supporting forest conservation and sustainable land use.
These climate finance derivatives provide innovative tools for various industries to address the risks posed by climate change while promoting sustainable development and environmental protection.
ccarbon App: The Most Convenient Carbon Inclusivity Management Platform
By leveraging the universality and compliance characteristics of CCT as a financial instrument, the ccarbon Climate Fintech Laboratory, combined with software development, provides society with comprehensive solutions for carbon asset certification, carbon asset trading, and management. The economic scale effect generated by the user base significantly reduces the cost of individual carbon asset certification.
Through the carbon reduction solutions provided by ccarbon, every carbon-reducing action generates corresponding economic incentives for the individual. The economic model supporting this is realized through the ccarbon Foundation’s financial asset trading and management in the climate finance market via CCT.
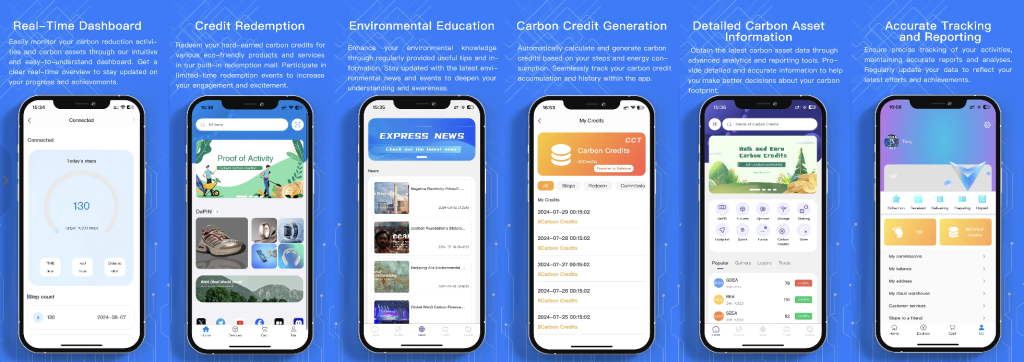
Welcome to ccarbon, a revolutionary application that combines smart wearables with converting your daily steps and energy consumption into valuable carbon credits. Embrace a healthier lifestyle with ccarbon while actively contributing to environmental protection.
Features:
– Real-Time Dashboard: Easily monitor your carbon reduction activities and carbon assets through our intuitive and easy-to-understand dashboard. Get a clear real-time overview to stay updated on your progress and achievements.
– Detailed Carbon Asset Information: Obtain the latest carbon asset data through advanced analytics and reporting tools. Provide detailed and accurate information to help you make better decisions about your carbon footprint.
– Professional Carbon Asset Market: Manage your personal carbon assets in a trusted professional carbon asset market. Easily buy, sell, and trade carbon credits while ensuring compliance with international carbon standards.
– Carbon Credit Generation: Automatically calculate and generate carbon credits based on your steps and energy consumption. Seamlessly track your carbon credit accumulation and history within the app.
– Credit Redemption: Redeem your hard-earned carbon credits for various eco-friendly products and services in our built-in redemption mall. Participate in limited-time redemption events to increase your engagement and excitement.
– Environmental Education: Enhance your environmental knowledge through regularly provided useful tips and information. Stay updated with the latest environmental news and events to deepen your understanding and awareness.
– Accurate Tracking and Reporting: Ensure precise tracking of your activities, maintaining accurate reports and analyses. Regularly update your data to reflect your latest efforts and achievements.
Our Vision:
We are committed to providing the most advanced carbon asset management tools to help you achieve your sustainability goals. Join us on a journey towards a healthy lifestyle and a green planet.
Download ccarbon now and start turning your steps into meaningful environmental impact!
ccarbon Carbon Reduction Smart Wearable Devices
In addition to the smart carbon reduction shoes mentioned in the first phase of the CCT carbon credit conversion pool, ccarbon also provide other smart wearable device solutions to manufacturers and brands of smart wearable devices, such as smart rings, smart bracelets, smart monitoring devices, etc. This helps traditional manufacturing enterprises transition to intelligent environmental protection while providing society with the infrastructure for a low-carbon, environmentally friendly lifestyle.
ccarbon’s empowerment of traditional manufacturing industries is an important strategy for sustainable development, offering a reference mechanism for cooperation with enterprises and node users.

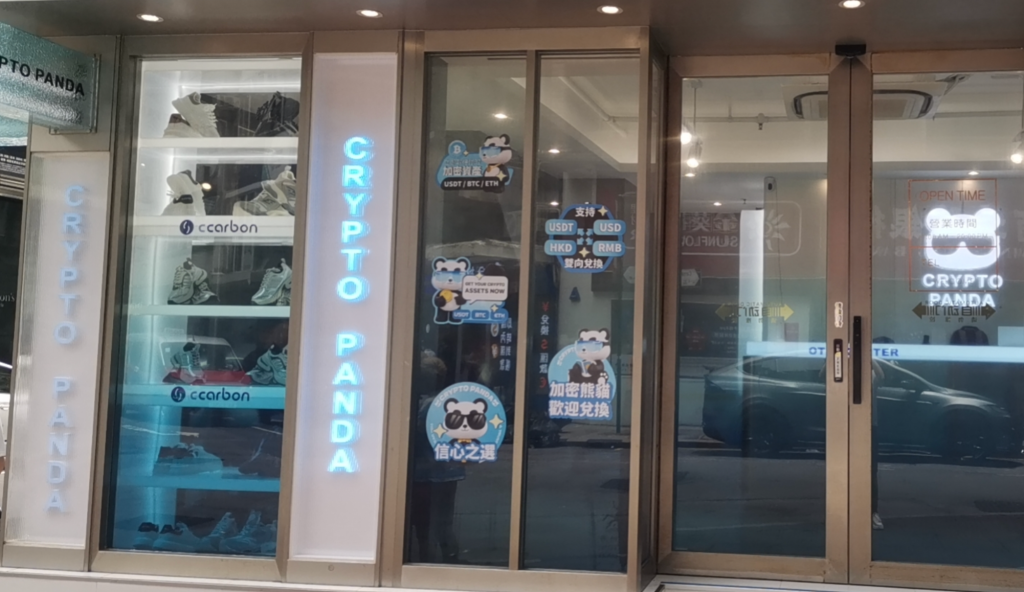
ccarbon has successfully upgraded its Asia-Pacific node to an ultra node and established the first ccarbon offline experience store at Shop 54-64B, Nathan Road, Tsim Sha Tsui, Hong Kong. This store allows ccarbon users to experience ccarbon DePIN products more intuitively. The low-carbon smart shoes are not just an innovative attempt by ccarbon in the field of personal carbon points; they are also the result of deep participation by the ccarbon laboratory. In the design and production of these products, ccarbon is committed to ensuring the green and sustainable development of the entire industrial chain. At the same time, through technological innovation and process improvement, ccarbon helps traditional manufacturing industries achieve green technology transformation, promoting the overall industry’s environmental upgrade.

Our Path

Contact Us:
ccarbon – Global Carbon Inclusivity Management Platform Official Website:
https://ccarbon.world
ccarbon Official Email:
Support@ccarbon.world
ccarbon – Global Carbon Inclusivity Management Platform APK Download (Requires Browser):
https://static.ccarbon.world/apk/ccarbon.apk
ccarbon – Global Carbon Inclusivity Management Platform iOS Public Beta Download:
https://testflight.apple.com/join/cKb2zGwF
ccarbon on X (Twitter):
https://x.com/ccarbonWorld
ccarbon Telegram Chinese Discussion Group:
https://t.me/ccarbonChinese
ccarbon Telegram Global Broadcast:
https://t.me/ccarbonWorld
Disclaimer
The information in this white paper is for reference only and does not constitute financial, investment, or professional advice. ccarbon Climate Fintech Laboratory makes no express or implied representations or warranties as to the accuracy, reliability, or completeness of the information contained herein.
Investing and trading in digital assets (including Carbon Credit Token, or CCT) involves significant risk and may result in the loss of your entire investment. You should conduct independent research, seek independent financial advice, and consider your own financial situation and risk tolerance before making any investment decisions.
This white paper does not constitute an offer to sell or solicit an offer to buy any securities or other financial instruments. Certain jurisdictions may have legal restrictions on the distribution of this white paper, and readers are responsible for ensuring compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
ccarbon App and CCT face various risks, including but not limited to technical risks, regulatory risks, market volatility, and operational risks. ccarbon Climate Fintech Laboratory cannot guarantee the success or future performance of the ccarbon App or CCT, and you should understand that the value of digital assets may fluctuate significantly.
Past performance is not indicative of future results. Any forward-looking statements in this white paper are based on assumptions and predictions that may change. ccarbon Climate Fintech Laboratory is under no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements.
By accessing this white paper, you acknowledge that you have read and understood this disclaimer and agree to be bound by its terms. If you do not agree to the terms of this disclaimer, you should not access or rely on the information in this white paper.
